Revolutionizing CAD Detection for All
A fast, non-invasive, radiation-free and evidence-based screening device for coronary artery disease: suitable for both symptomatic and high risk patients.

Fast, Accurate & Accessible CAD Screening
HeartForce™ enables earlier, smarter detection of coronary artery disease (CAD) across clinical settings. Our CAD screening assessments can be conveniently conducted in GP offices, pharmacies, ambulances, sport clubs, the military and emergency rooms or cardiology units of hospitals.

The Limitations of Current CAD Tests
- Conventional stress tests often miss early-stage or asymptomatic disease
- Imaging tests are expensive and limited in accessibility
- Most tests detect the disease only after symptoms occur

Evidence-Based Cardiac Risk Assessment, Beyond Symptoms
The CardioClin™ test, utilizing the Electro-mechanical CAD Risk Score (EMCR Score™) technology, detects individuals at risk, regardless of whether they have chest pain, breathing issues, or show no symptoms at all.
Clinical studies show superior performance to existing CAD screening methods and diagnostics tests like the stress ECG and Calcium test (CACS)⁵, making CardioClin™ a reliable tool for proactive care.
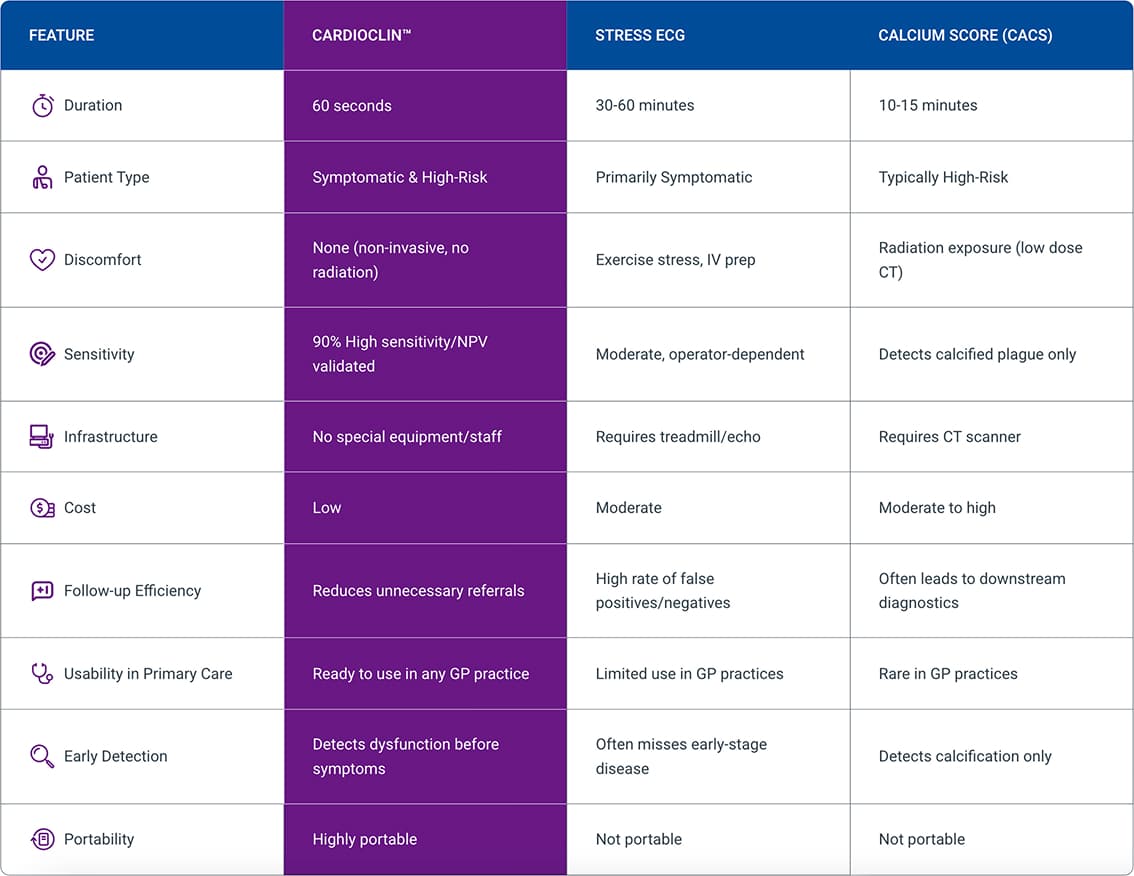
CardioClin™ vs. Traditional CAD Tests
Feature | CardioClin™ | Stress ECG | Calcium Score (CACS) |
|---|---|---|---|
Duration | 60 seconds | 30-60 minutes | 10-15 minutes |
Patient Type | Symptomatic & High-Risk | Primarily Symptomatic | Typically High-Risk |
Discomfort | None (non-invasive, no radiation) | Exercise stress, IV prep | Radiation exposure (low dose CT) |
Sensitivity | 90% High sensitivity/NPV validated | Moderate, operator-dependent | Detects calcified plaque only |
Infrastructure | No special equipment/staff | Requires treadmill/echo | Requires CT scanner |
Cost | Low | Moderate | Moderate to high |
Follow-up Efficiency | Reduces unnecessary referrals | High rate of false positives/negatives | Often leads to downstream diagnostics |
Usability in Primary Care | Ready to use in any GP practice | Limited use in GP practices | Rare in GP practices |
Early Detection | Detects dysfunction before symptoms | Often misses early-stage disease | Detects calcification only |
Portability | Highly portable | Not portable | Not portable |
Key Benefits of the CardioClin™ Screening Test
HeartForce™ empowers health professionals to respond quickly and with assurance, and gives patients and their loved ones what they need most: peace of mind.
From fast results to easy access, we tailor each benefit to enhance decision-making and facilitate timely interventions.

Time-Saving
Results in just 60 seconds: enables rapid triage and faster clinical decisions
Affordable
Reduces the need for expensive diagnostic equipment and overburdened specialists
Reliable
Clinical studies showing superior performance vs. existing tests
Scalable
Easily deployable across care settings, without infrastructure overload
Accessible
Works in primary care, clinics, pharmacies, emergency care, and cardiology units.
Non-Invasive
No needles, no radiation, no discomfort. Safe for routine and preventive use
Find Your Direction
For Healthcare Professionals
Understand how our Electro-mechanical CAD Risk Score technology, including seismography, supports confident CAD screening.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the CardioClin™ CAD screening test?
The CardioClin™ is a compact, cost-effective, and AI-powered device that measures the mechanical activity of the heart to assess the risk of coronary artery disease (CAD). It provides a quick and easy option compared to traditional health screening tests. Suitable for first line practices, diagnostic centers, emergency departments, and cardiology units, etc.
How long does the CAD test take?
The CardioClin™ screening process is designed for efficiency in clinical workflows. From setup to results, it takes just 5–10 minutes, with only 60 seconds of cardiac data acquisition. The test is completely non-invasive, easy to perform, and provides immediate, reliable insights to support CAD risk assessment and triage decisions.
Who should consider taking the CAD test?
CardioClin™ CAD testing is appropriate for individuals presenting with symptoms suggestive of coronary artery disease, such as chest discomfort, shortness of breath, or unexplained fatigue, as well as for high-risk patients with multiple CAD-associated risk factors, even when symptoms are mild or absent. Relevant risk factors include hypertension, hyperlipidaemia, diabetes, obesity, smoking, and a family history of heart disease.
How is CardioClin™ different from other CAD tests?
CardioClin™ uses seismocardiography (SCG) to capture the heart’s mechanical activity (micro-vibrations caused by cardiac contraction and valve motion), and applies an AI-driven algorithm, the Electro-Mechanical CAD Risk (EMCR) Score™, to estimate CAD risk. Unlike conventional tests that rely on imaging, radiation, or exercise stress, CardioClin™ provides a rapid, non-invasive, 60-second functional screening that integrates physiological data with clinical risk factors. It supports earlier, more efficient CAD risk stratification and helps reduce unnecessary diagnostic testing.
Contact Us
Looking to improve patient outcomes and reduce unnecessary testing with a scalable, cost-effective, and patient-friendly CAD screening solution?
References
- Dehkordi P, Tavakolian K, Xiao ZG, Khosrow-Khavar F. Introducing the Electromechanical Risk Factor Score derived from seismocardiography for estimating the likelihood of coronary artery disease. In: Computing in Cardiology (CinC); 2023.
- Dehkordi P, Tavakolian K, Xiao ZG, Yuldashov A, Khosrow-Khavar F. Assessing coronary artery disease risk using seismocardiography in patients with chest pain. In: 2025 IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC); 2025 July 15–19; Milan, Italy. IEEE; 2025.
- Roth GA, et al. Global, regional, and national burden of cardiovascular diseases and risk factors in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2023. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2025;76(12):1452–78. Available from: https://www.acc.org/latest-in-cardiology/journal-scans/2025/09/24/21/17/new-global-burden
- Piepoli MF, Hoes AW, Agewall S, et al. 2016 European Guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32119297/
- Nelson, A. J., Ardissino, M., & Psaltis, P. J. (2019). Current approach to the diagnosis of atherosclerotic coronary artery disease: More questions than answers. Therapeutic Advances in Chronic Disease, 10, 1–20. https://doi.org/10.1177/2040622319884819